
Intel vs AMD processors – 8th generation Intel Core Coffee Lake vs AMD Ryzen processors (CPUs)

Intel vs AMD – The AMD Ryzen CPU ranges
2017 saw the usual Intel vs AMD situation reverse. AMD recaptured the lead from Intel in the high-end desktop-PC processor market with its Ryzen range of CPUs that employ the new Zen processor micro-architecture. AMD hasn’t enjoyed such a lead since the days of Intel Slot 1 and AMD Slot A processors of 1998/1999. Indeed, George W. Bush was US president when AMD last gave Intel any competition in the high-end CPU market. The company’s share of the CPU market has increased slightly as a result. All of the Ryzen desktop-PC models provide superior bang-for-buck performance against the latest equivalent Intel Core (Coffee Lake) CPUs. Moreover, the mobile laptop versions of the Ryzen processors look set to give Intel strong competition in the laptop market for the first time.
Ryzen models
The Ryzen range that is responsible for making AMD seize the Intel vs AMD crown from Intel consists of the following models – the high-end Threadripper (1950X, 1920X, 1900X) the performance Ryzen 7 (1700 to 1800X, the mainstream Ryzen 5 (1400 to 1600X) and the entry-level Ryzen 3 (1200 – to 1300X).
Note that the Ryzen CPUs do not provide a built-in graphics chip, which the 8th-generation Coffee Lake Core processors all provide. Therefore, if you don’t want to use a separate graphics card, you can make up for AMD’s lower-priced CPUs, if you are self-building, by using a low-end i3 Coffee Lake CPU. However, most self-builders of high-end desktop PCs want the whole system to be high-end, which means using one or more high-end graphics cards.
Since the Ryzen 3, 5 and 7 models have the same numbers as the Intel Core i3, i5 and i7, AMD must regard them as being its equivalent offerings. For both Intel and AMD, the 3 models are low-end, the 5 models are mid-range and the 7 models are high-end.
The Ryzen 7 1700 is a particularly good bargain
The Ryzen 7 1700 is a particularly good bargain with eight cores and sixteen threads (using Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) technology), running at a stock speed of 3.7 GHz, for just £230/$294 (Amazon December 14, 2017). Read further down about overclocking the unlocked Ryzen CPUs.
Amazon purchaser review: “This thing is amazing! I am running it as a Linux KVM server running between 20-30 virtual machines and it handles them all extremely well. This is most noticeable with rebooting where it manages to start all the VMs up in seconds. It also does an amazing job at converting videos with ffmpeg and at a 65 Watt TDP and a fantastic bundled cooler, you never hear the darn thing! I wish I had the money to buy more!”
Ryzen 3, 5, 7 Pro processors
Note that by March 2020 AMD had released the third generation of Ryzen 3, 5 and 7 CPUs for the desktop PC. Therefore, if you want a PC with one of the latest versions, make sure that it is a third-generation chip or a higher generation chip at a later date. The vendors might have unsold earlier-generation chips that they want to get rid of by passing them off as being of the latest generation.
AMD Ryzen CPUs – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ryzen
Here are the specifications of the top first generation model : AMD Ryzen™ 7 PRO 1700X
Number of CPU Cores: 8
Base Clock Speed: 3.4GHz
Max Turbo Core Speed: 3.8GHz
Required power supply : 95 Watts
Socket AM4 and Socket TR4
All of the models require a Socket AM4 motherboard except the high-end Threadipper models that use the new Socket TR4.
The Threadipper models are AMD’s first LGA (Land Grid Array) CPUs for the desktop PC that have the pins in the socket and metal contacts on the CPU itself. All of Intel’s desktop-PC models use LGA technology, starting with the Pentium 4 (Prescott) in 2004. Pin Grid Array (PGA) CPUs have the pins on the processor itself that fit into a grid array in the socket.
The manufacture of all of the Ryzen CPUs employ the latest 14nm fabrication process and employ AMD’s version of Intel’s Hyper-Threading technology – Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) technology – which provides a virtual core for every actual core by running two threads per core. Using it, a quad-core Ryzen CPU operates as if it has eight cores.


Unlocked CPU clock multipliers and auto-overclocking
All of the Zen-powered AMD APU CPUs provide a built-in graphics chip, but none of the Ryzen CPUs have a built-in graphics chip. To provide graphics output, they require either a separate graphics card or a graphics chip that the PC’s motherboard provides.
The Ryzen clock multipliers that set the processor’s speed are *all* unlocked, which means that their settings can change to provide speeds higher than the stock speed. Indeed, the Ryzen CPUs all support automatic overclocking (auto-overclocking). If the model has an X in its name, it provides 100Mhz of overclocking compared to 50Mhz for the other models. The high-end Threadipper models – all X models – provide 200Mhz of auto-overclocking. In short, if the computer is able to deliver extra operational speed, it does so automatically. The user is also able to use UEFI BIOS settings to increase the clock multiplier and CPU voltages in order to achieve manual overclocking.
Note that you must always research the overclocking of a particular model of CPU before implementing it, because if you overclock it too far you can destroy it.
Current Prices and purchaser reviews on Amazon
Get an idea of the current pricing on Amazon for all of the Ryzen models, including the Threadipper 8, 12 and 16 core models. Read the purchaser reviews. Then shop around. There are many YouTube videos on the Ryzen desktop CPUs.
AMD Ryzen laptops
Laptops that run the mobile versions of the Ryzen CPUs – AMD Ryzen Mobile Processors with Radeon Vega Graphics – are available. Reviewers are saying that AMD is now giving Intel serious competition in the laptop market for the first time. There are many YouTube videos on the Ryzen mobile CPUs.
AMD Is Crushing Intel in Laptops Too?? – ASUS Zephyrus GA502 Review –
Ryzen page on Wikipedia
For more detailed technical information on AMD’s new processor range, visit the following Wikipedia page.
Ryzen – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ryzen
Intel vs AMD – Intel Core i7, i5 and i3 Coffee Lake processors
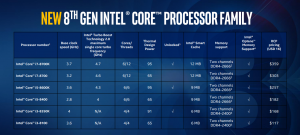
The 8th generation Intel Coffee Lake CPUs use the same core design and the latest 14nm fabrication process as the 7th generation Kaby Lake CPUs, but employ more cores and improved performances. More cores means needing more power, which means running the new CPUs from a *new* motherboard with a new chipset. The Coffee Lake models still use a Socket 1151 motherboard, but, due to changes in the number of cores, their speed (frequency) increases and the extra power required, the Socket 1151 motherboard must have the 300-series chipset.
The image of a table above shows some of the specifications and the prices at a particular date. In spite of those improvements compared to the previous generation chips, the Coffee Lake processors provide less bang-for-buck than equivalent AMD Ryzen chips. Get an idea of the current prices on Amazon, then shop around.
At the time of writing, 6 Coffee Lake processors were available – two models each for the i7, i5 and i3 ranges.
Coffee Lake CPUs provide a built-in graphics chip
Note that the Coffee Lake CPUs provide a built-in graphics chip, which none of the Ryzen CPUs provide. The graphics is adequate for most computing tasks, but is not adequate for graphics-intensive tasks, such as playing high-end PC games. For example, you will probably have to disable the motion blur and anti-aliasing settings and reduce the screen resolution to 720p in order to get a playable frame-rate. A 3D game played at a frame-rate of 36fps only chugs along.
Nevertheless, if self-building a desktop PC, you can make savings that make up for the cheaper Ryzen CPUs, by building a low-end system using a Core i3 model that uses its built-in graphics instead of a separate graphics card.
The Coffee Lake Core i7 and i5 models have 6 cores instead of 4, which means that Intel’s Hyper-Threading technology allows them to use another 6 virtual cores. The Core i5 models don’t provide Hyper-Threading. The Coffee Lake Core i3 models have dropped Hyper-Threading but have 4 cores compared to the 2 cores of the Kaby Lake models, so they can process the same number of threads as the previous generation i3s.
Coffee Lake laptop CPUs
No information was available on Kaby Lake laptop models, the arrival of which always lags behind the desktop models. In December 2017, the top laptop from Lenovo, model Ideapad 320S-14IKB 81BN004WSB, runs the Intel Core i7-8550U (Kaby Lake) 7th-generation processor.
For more detailed technical details, including the differences between the Coffee lake and Kaby Lake CPUs, visit the following Wikipedia page.
Coffee Lake – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coffee_Lake
Intel vs AMD – Overclocking the Coffee Lake processors
The 300-series chipset, which makes it possible to run the Coffee Lake CPUs on a Socket 1151 motherboard, allows the maximum Turbo Boost ratio for each core to be set individually. This feature allows you to run every core at the maximum speed it can support stably.
Always remember to research the overclocking of any processor in order to find out what its limits are before experimenting with it.
Intel vs AMD to date – Conclusion
Intel’s Coffee Lake CPUs are superior to the Kaby Lake versions, but not improved enough for Intel to take the crown, recently-won, back from AMD.
Other related posts and pages on this website
POST: AMD Ryzen 3, 5 and 7 processors (CPUs) strike back hard at Intel dominance
POST: How to decode Intel/AMD processor names – What processor names mean
PAGE: Processor Sockets – Intel and AMD Socket Types
PAGE: The Intel and AMD processors (CPUs) used in desktop PCs